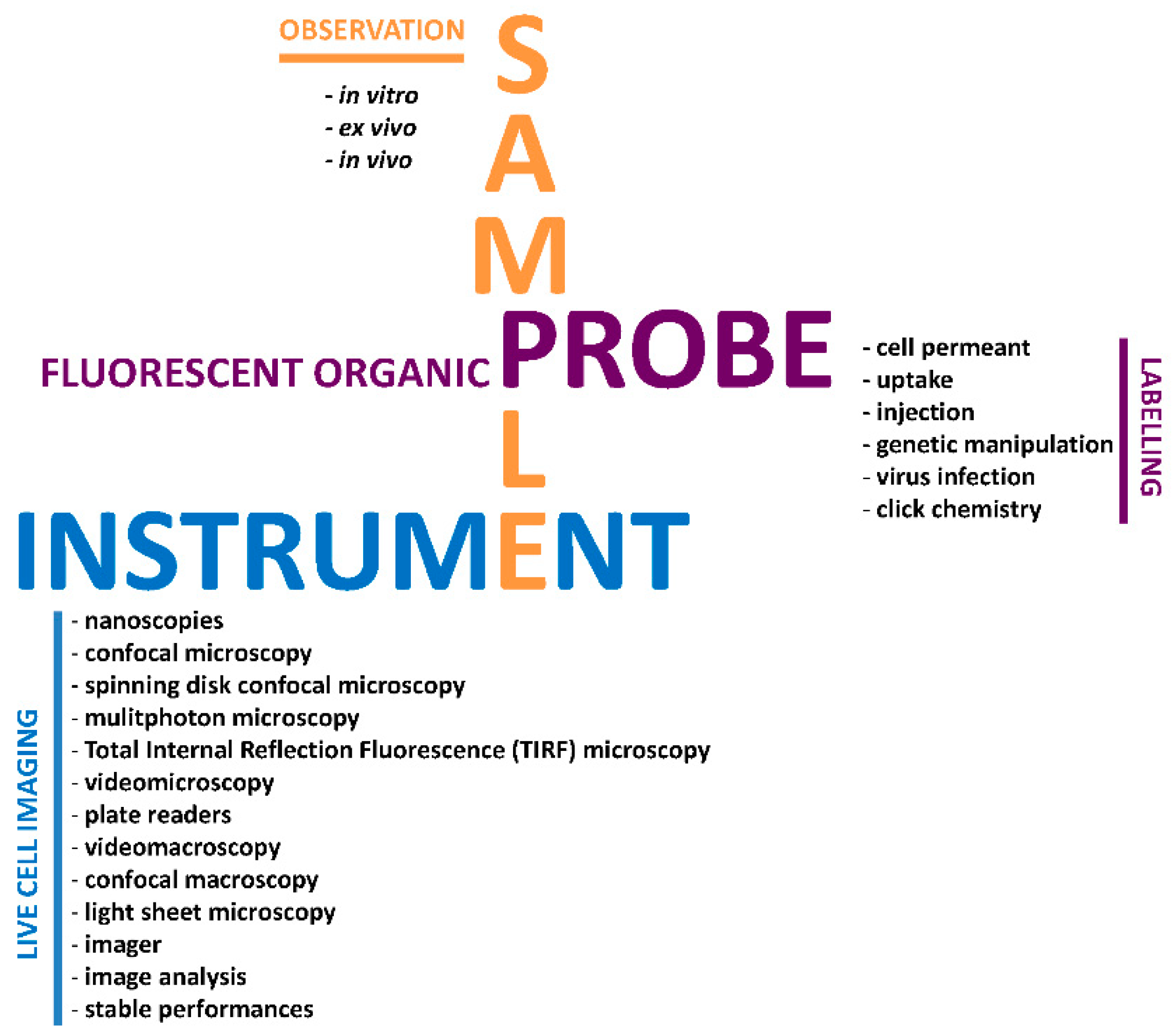
44 fluorescent labels and light microscopy
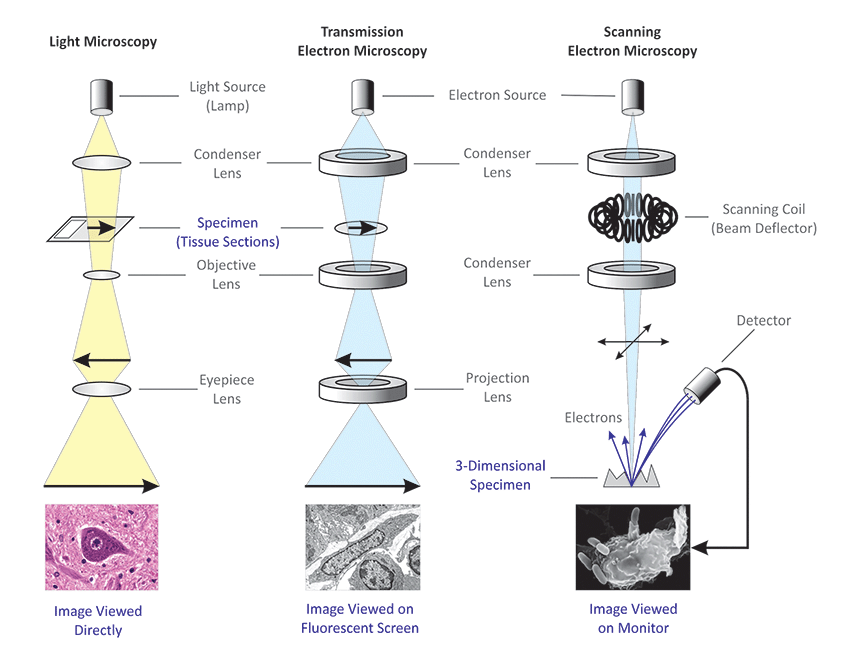
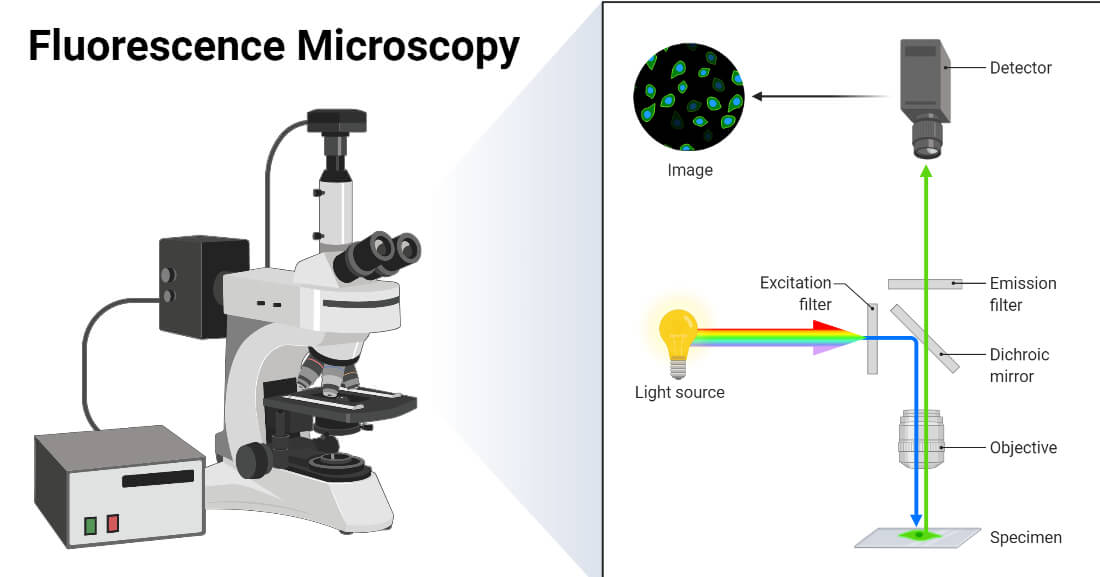
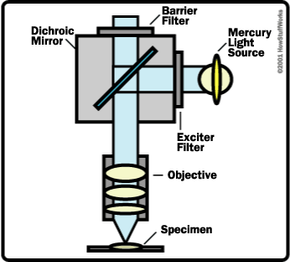
Fluorescence microscope - Wikipedia The majority of fluorescence microscopes, especially those used in the life sciences, are of the epifluorescence design shown in the diagram.Light of the excitation wavelength illuminates the specimen through the objective lens. The fluorescence emitted by the specimen is focused to the detector by the same objective that is used for the excitation which for greater resolution will need ... Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells March 7, 2022 Researchers have developed a new fluorescent label that gives a clearer picture of how DNA architecture is...
Fluorescence Microscopy vs. Light Microscopy - News-Medical.net This means that fluorescent microscopy uses reflected rather than transmitted light. For example, a commonly used label is green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is excited with blue light and...
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy
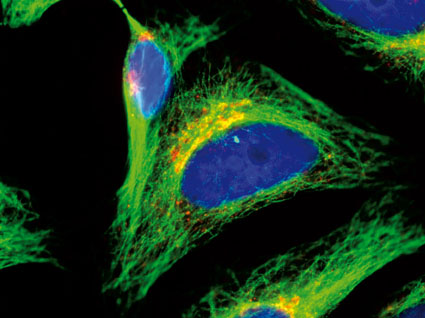
Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy • iBiology In this introductory lecture on light microscopy, Dr. Nico Stuurman describes the principles and properties of fluorescence microscopy. Skip to primary navigation; ... 00:01:04;23 so we label microtubules with the fluorescent dye 00:01:08;13 and we have part of the cell labeled in red, 00:01:11;25 and that part is actually the uh, nucleus Fluorescent Labeling - What You Should Know - PromoCell Fluorescence microscopy allows the identification of cells and cellular components and the monitoring of cell physiology with high specificity. Fluorescence microscopy separates emitted light from excitation light using optical filters. The use of two indicators also allows the simultaneous observation of different biomolecules at the same time. New fluorescent label provides a clearer picture of how DNA ... Unlike traditional fluorescence microscopy, which uses labels that glow constantly, this approach involves switching on only a subset of the labels at each moment. ... Discovery of 380-million ...
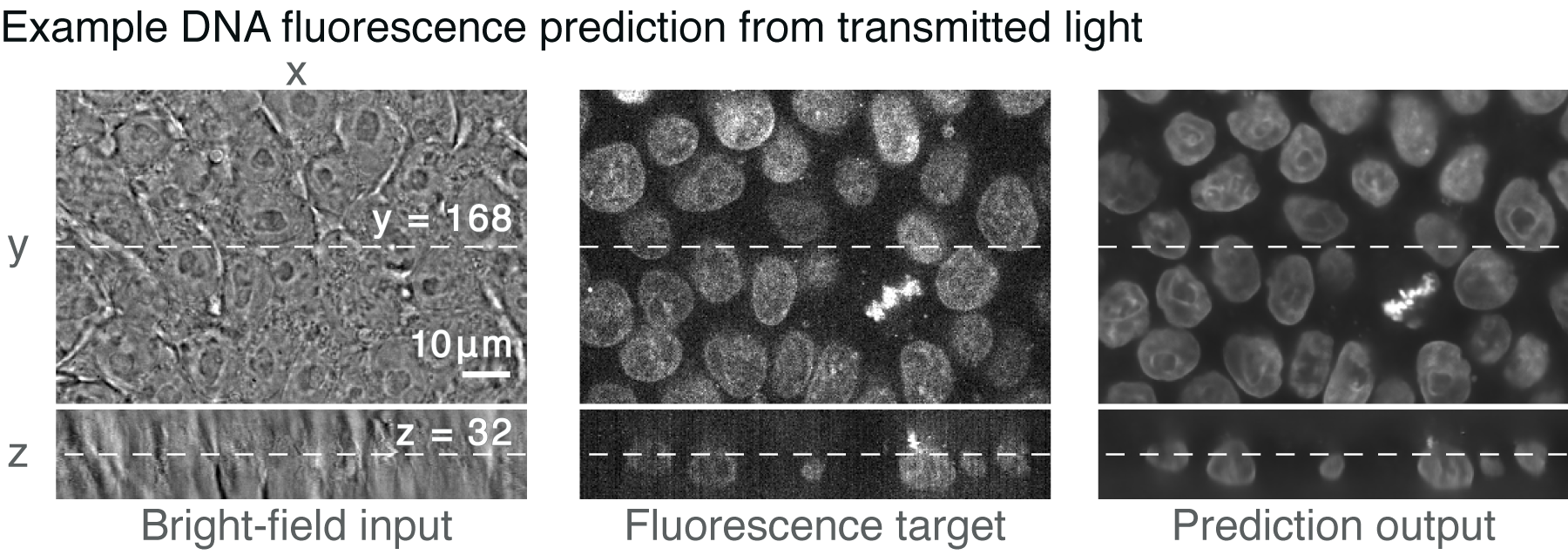
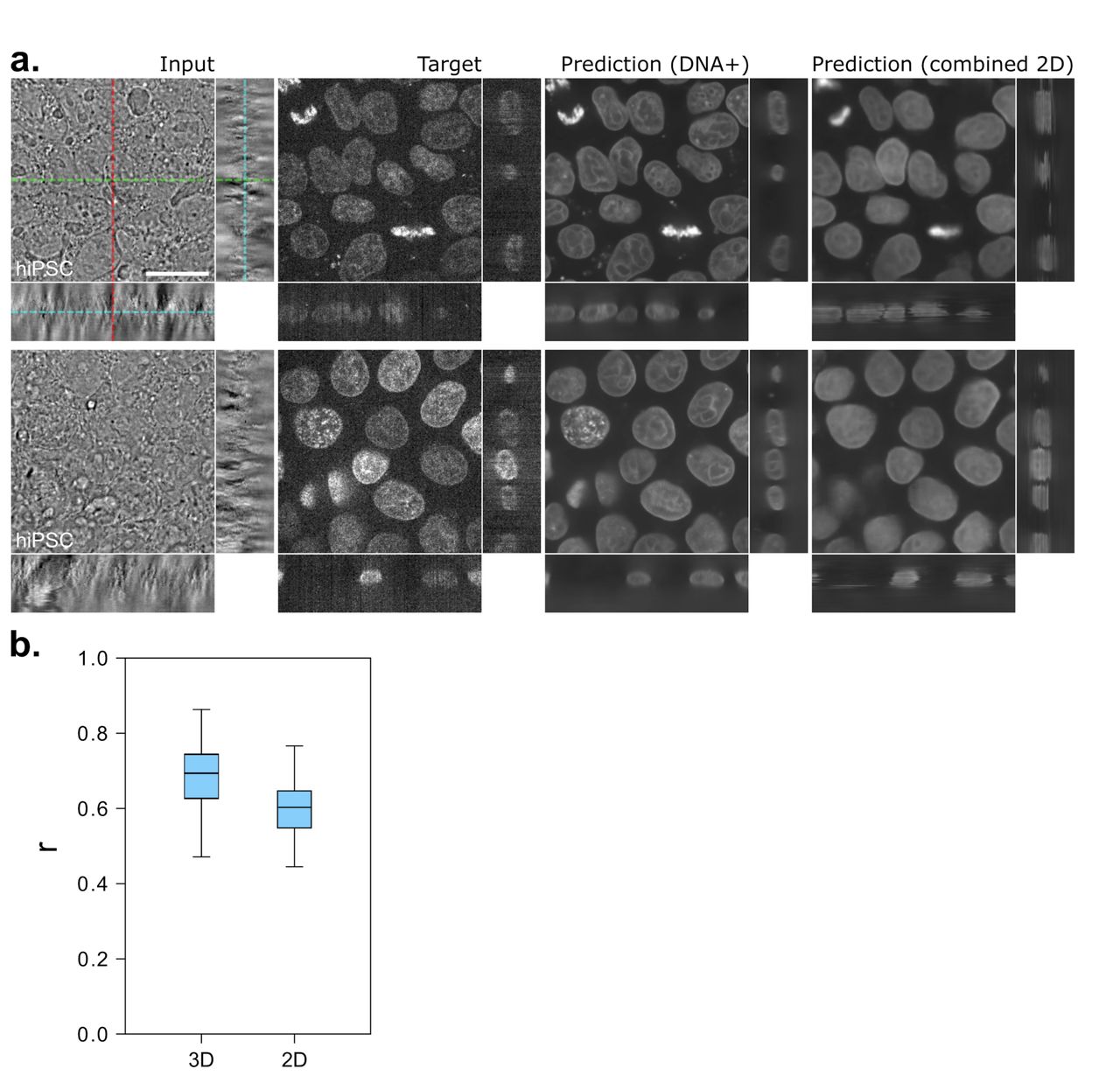
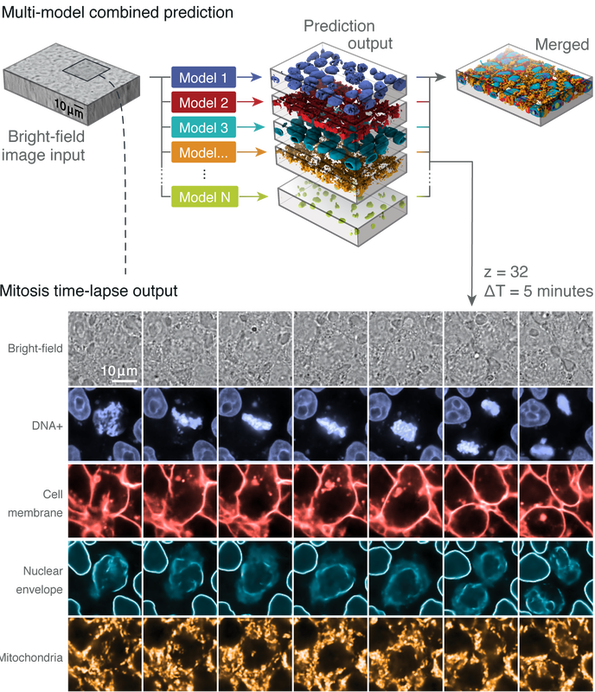
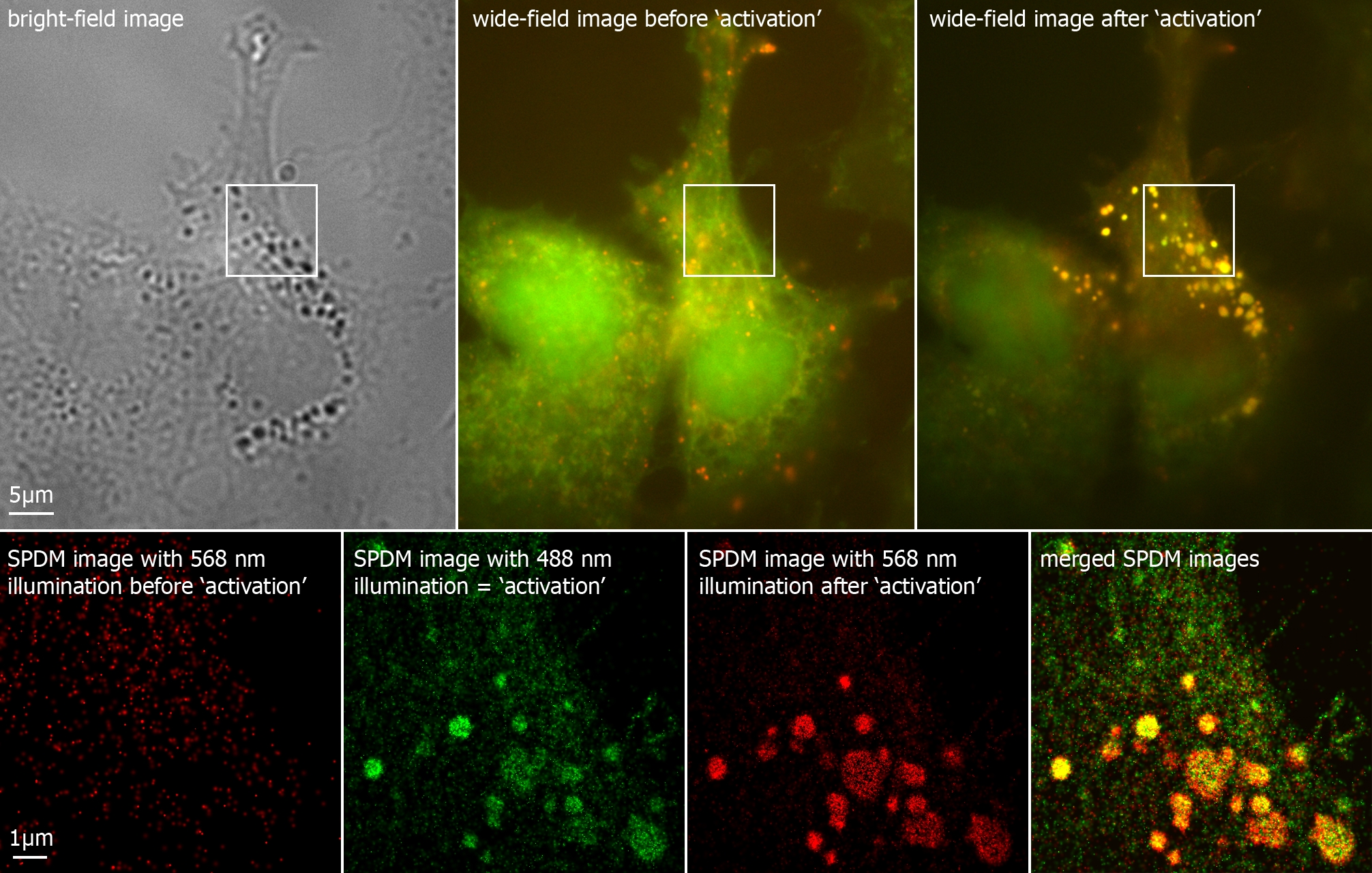
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy. In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled Images Microscopy is a central method in life sciences. Many popular methods, such as antibody labeling, are used to add physical fluorescent labels to specific cellular constituents. ... (ISL), reliably predicts some fluorescent labels from transmitted-light images of unlabeled fixed or live biological samples. ISL predicts a range of labels, such as ... Researchers demonstrate label-free super-resolution microscopy - Phys.org A newly developed sub-diffraction-limit microscopy approach doesn't require fluorescent labels. The video shows the process of the data evaluation algorithm, retrieving the positions and sizes of... Fluorescent Microscopy A fluorescence microscope is much the same as a conventional light microscope with added features to enhance its capabilities. The conventional microscope uses visible light (400-700 nanometers) to illuminate and produce a magnified image of a sample. A fluorescence microscope, on the other hand, uses a much higher intensity light source which ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › FluorescenceFluorescence - Wikipedia A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to ...
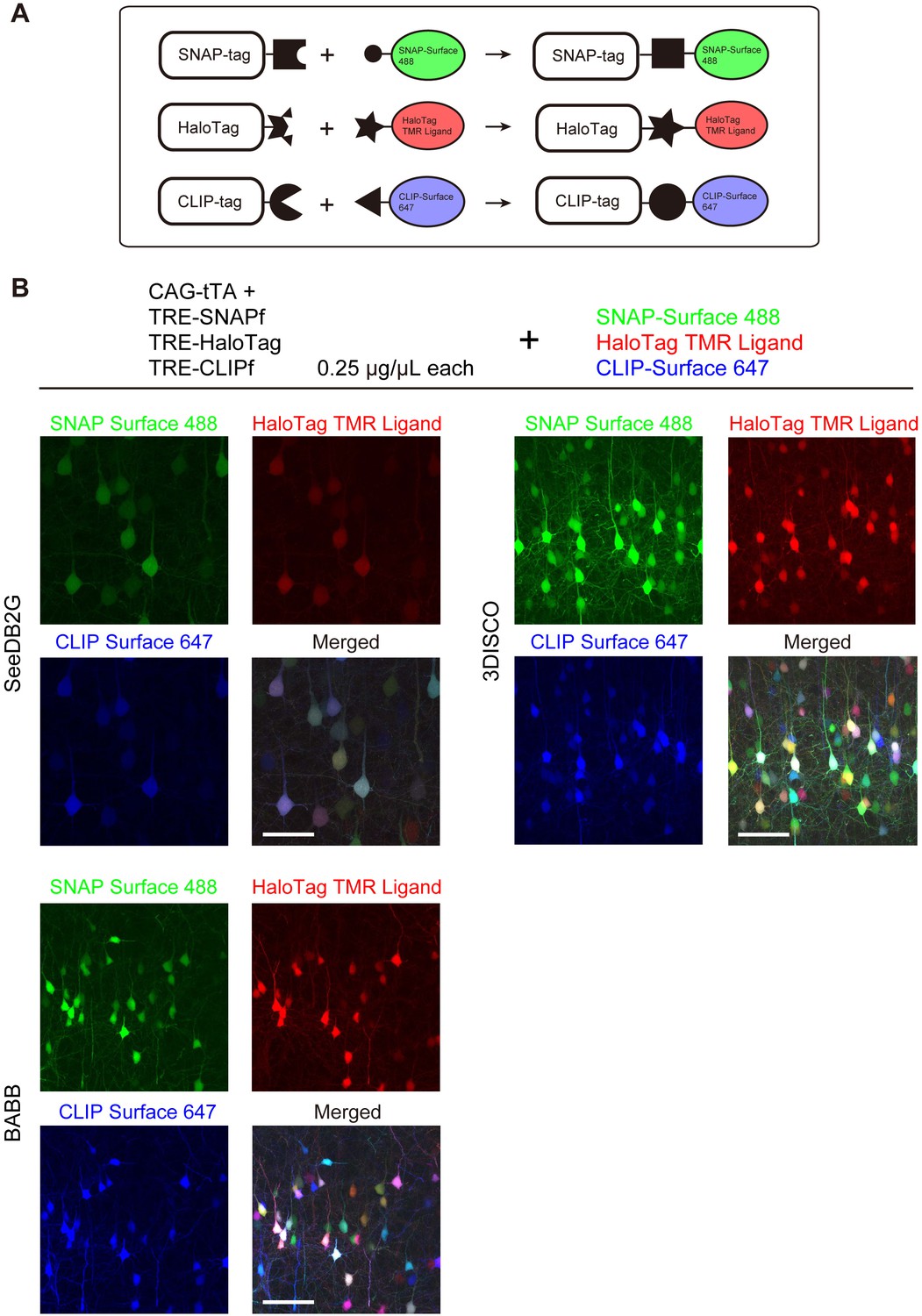
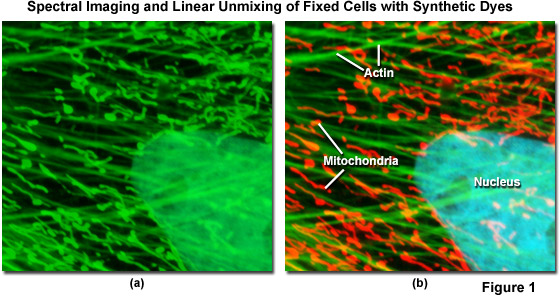
Fluorescence Microscopy & Cell Imaging | Research | UNM Cancer Center Fluorescence microscopy is routinely used to determine spatial and topological information about cells and tissues. Sophisticated laser scanning microscopic instrumentation, ultra sensitive digital cameras and specialized fluorescence probes make it possible to visualize cellular events in real time down to the molecular level. Fluorescent tag - Wikipedia S. cerevisiae septins revealed with fluorescent microscopy utilizing fluorescent labeling In molecular biology and biotechnology, a fluorescent tag, also known as a fluorescent label or fluorescent probe, is a molecule that is attached chemically to aid in the detection of a biomolecule such as a protein, antibody, or amino acid. Dots, Probes and Proteins: Fluorescent Labels for Microscopy and Imaging There are currently 20 AlexaFluor dyes which span the excitation spectrum from 346 nm to 784 nm and are available as labelling kits, or conjugated to primary or secondary antibodies. Thermo Scientific produce their own probes called ' DyLight '. The ten probes which are currently available cover a spectrum from 350 nm to 800 nm. Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics M. Heilemann, in Comprehensive Biophysics, 2012 Abstract. Fluorescence microscopy is a valuable toolbox to study cellular structures and dynamics spanning scales from the single molecule to the live animal. The spatial resolution that can be achieved with any light-based microscopy is however limited to about 200 nm in the imaging plane and >500 nm along the optical axis.
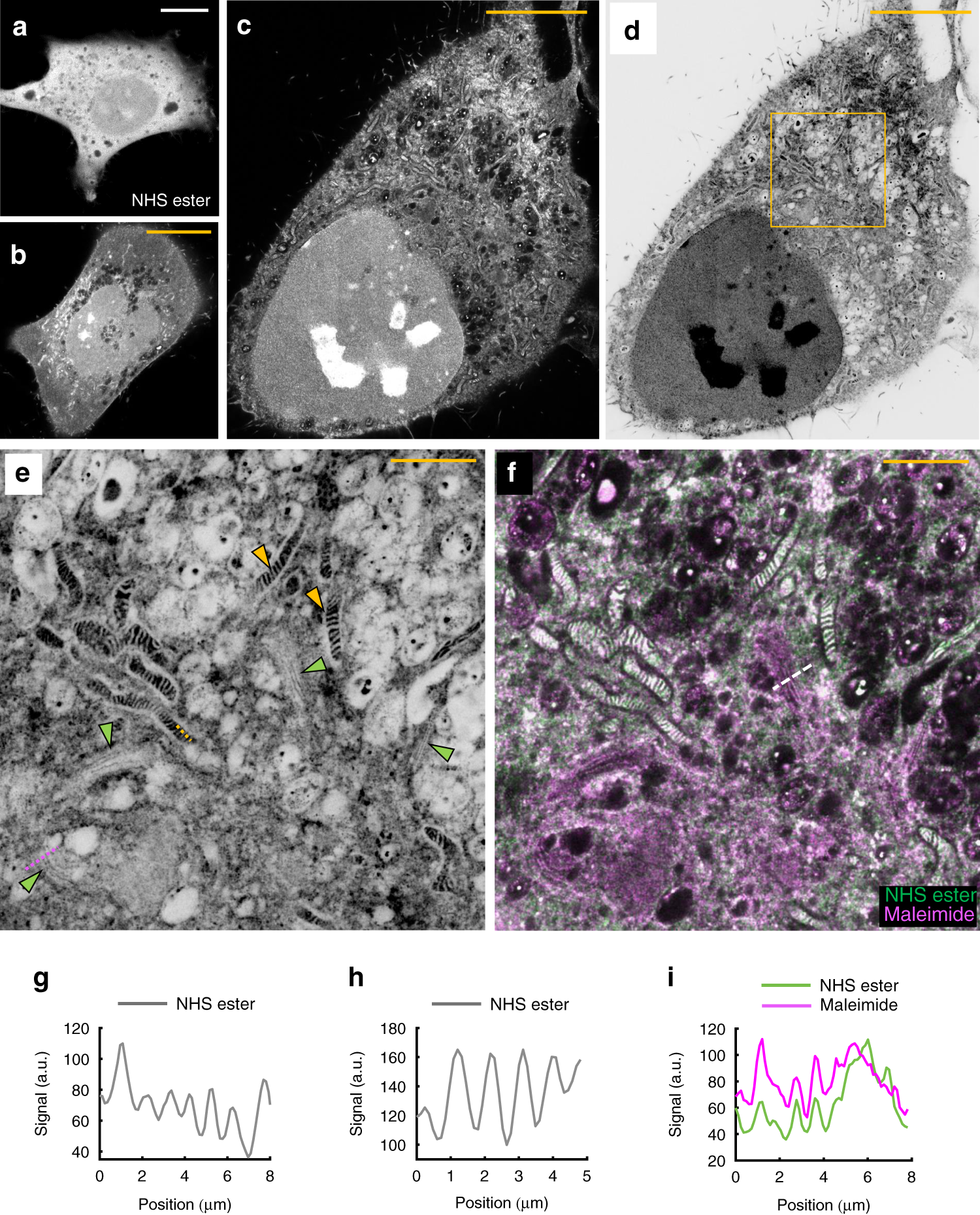
In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled ... - Cell The z-stacks of transmitted-light microscopy images were acquired with different methods for enhancing contrast in unlabeled images. Several different fluorescent labels were used to generate fluorescence images and were varied between training examples; the checkerboard images indicate fluorescent labels that were not acquired for a given example. Fluorescence Microscope: Principle, Types, Applications Fluorescence microscopy is a light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation (such as UV light) and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light (such as green or red light). This phenomenon, also called fluorescence ... › newsFluorescent Nanodiamonds for HeLa Cell Drug Delivery Aug 24, 2022 · The developed fluorescent nanodiamonds were characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and secondary electron microscopy. Compared to the free drug with drug release in 12 hours, the fluorescent nanodiamonds functionalized with drug molecules exhibited sustained drug release for over 72 hours. Imaging Flies by Fluorescence Microscopy: Principles, Technologies, and ... Fluorescence microscopy in combination with specific labeling methods [ e.g., antibodies or fluorescent proteins (FPs)] enables selective visualization of the components of living matter, from molecules and organelles to cells and tissues, in both fixed and living organisms, and with high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
› doi › 10Semiconductor Nanocrystals as Fluorescent Biological Labels Sep 25, 1998 · In addition, nanocrystal probes may prove useful for other contrast mechanisms such as x-ray fluorescence, x-ray absorption, electron microscopy, and scintillation proximity imaging, and the use of far red– or infrared-emitting nanocrystals (InP and InAs) as tunable, robust infrared dyes is another possibility.
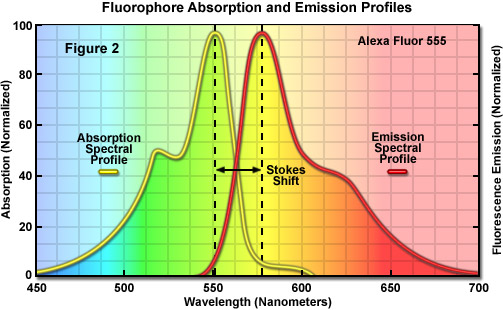
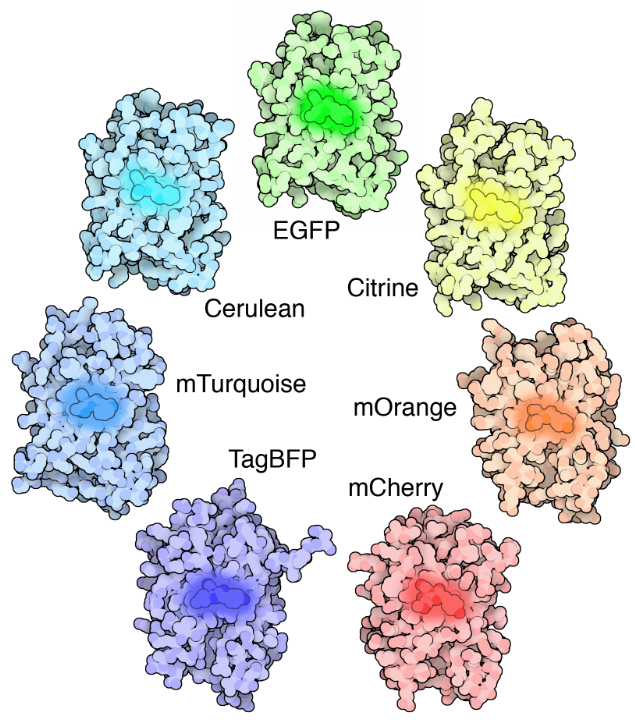
› techniques › fluorescenceIntroduction to Fluorescent Proteins | Nikon’s MicroscopyU The brightness and fluorescence emission spectrum of enhanced yellow fluorescent protein combine to make this probe an excellent candidate for multicolor imaging experiments in fluorescence microscopy. Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein is also useful for energy transfer experiments when paired with enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (ECFP) or ...
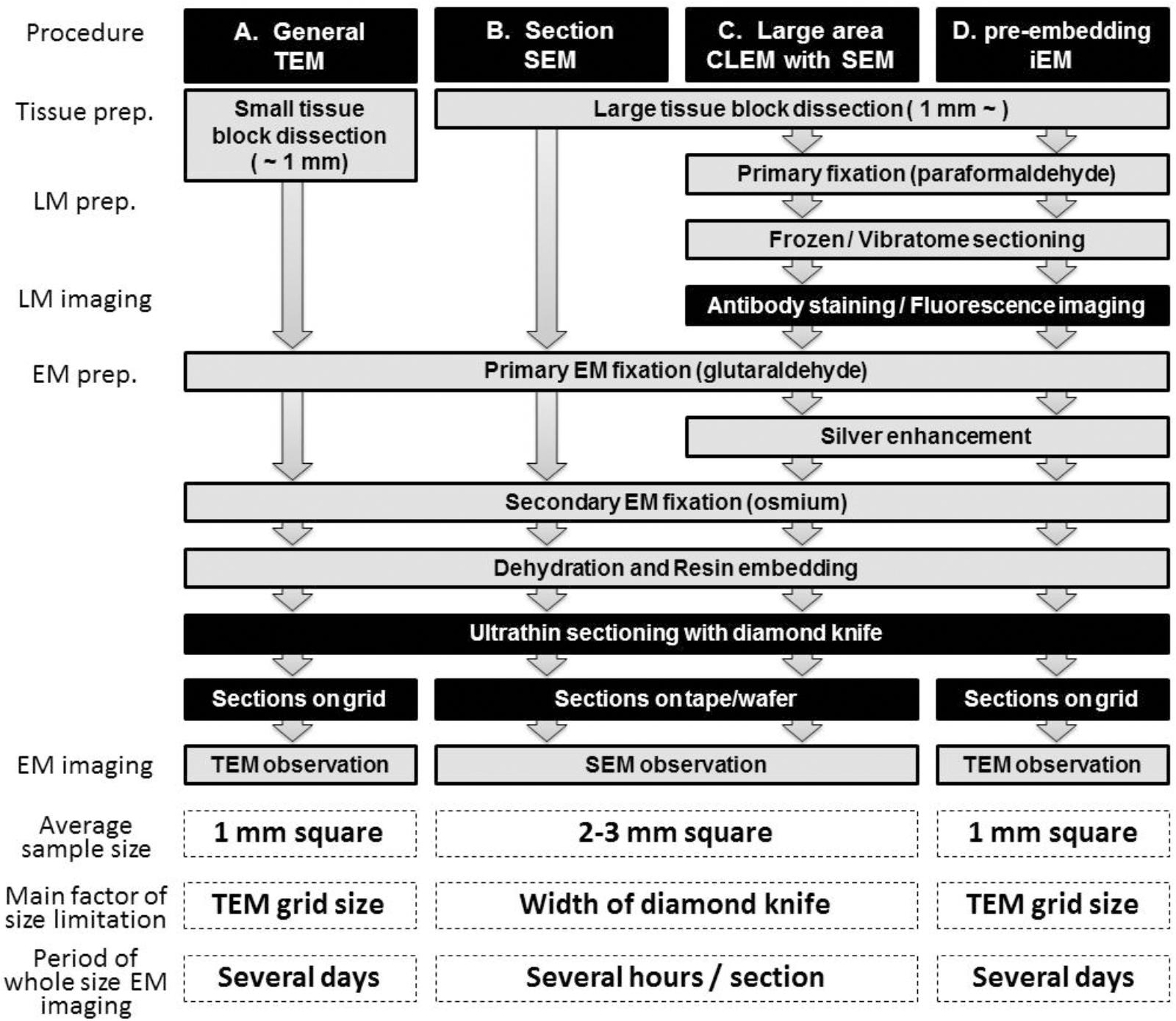
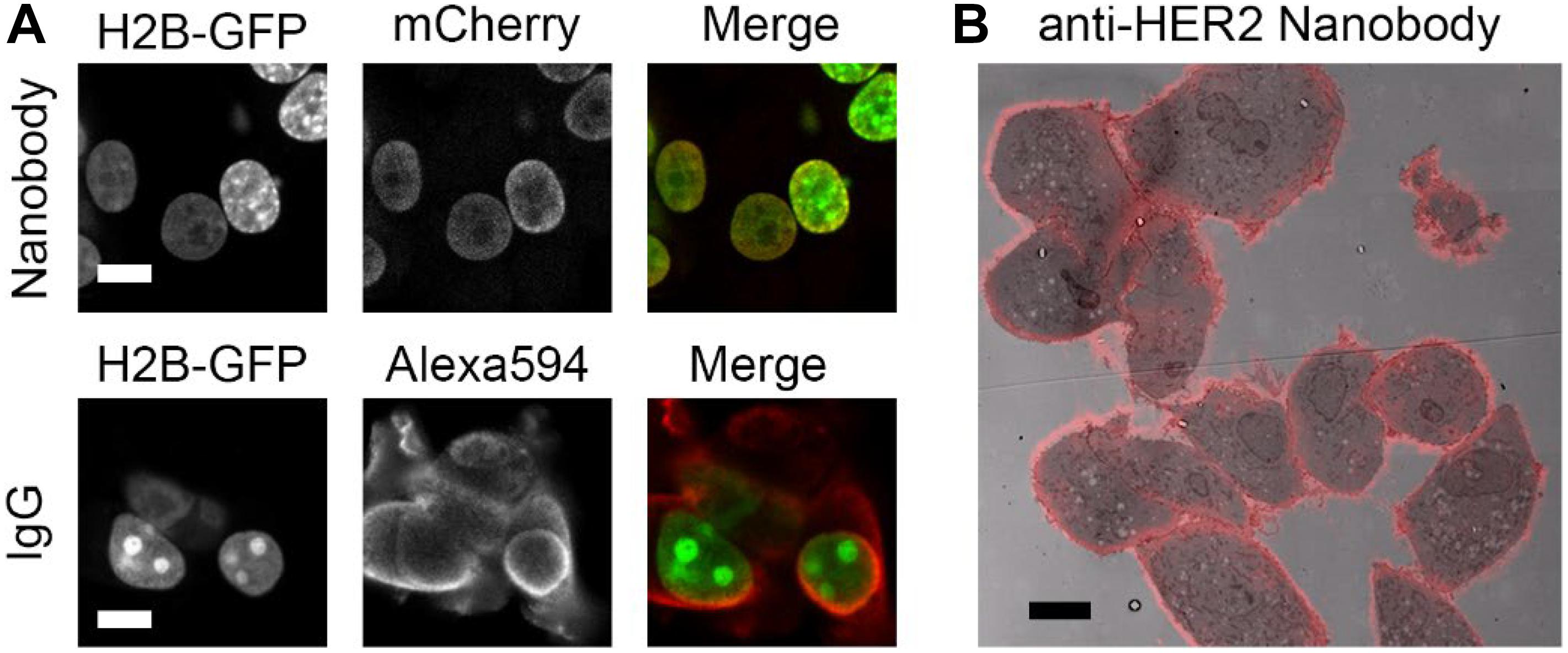
Immunolabeling for Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy on ... An ideal label for light and electron microscopy would contain both fluorescent dye and a colloidal nanoparticle on a single antibody molecule. Secondary and tertiary label, the colloidal nanoparticles are placed on the primary antibody while the fluorescent dye conjugated to secondary ( D) or tertiary ( E) antibody.
› products › pMica | Products | Leica Microsystems No constraints - Select the right modality in real time. Mica unifies transmitted and fluorescence light imaging modalities. You can select from multiple imaging modalities all within one Microhub, including widefield, confocal, THUNDER imaging, LIGHTNING, Z-stacks, time-lapse and more.
Fluorescence Microscopy: In-Line Illumination with Imaging Filters Fluorescence microscopy is ideal for measuring and analyzing the absorption and excitation of various wavelengths of light. An in-line fluorescence microscopy setup utilizes a plate beamsplitter to redirect light from an illuminator into the parallel optical path. Mechanically, this setup is less complex than some other digital video microscope ...
Fluorescence Imaging - Teledyne Photometrics Fluorescent molecules (known as fluorophores) are used to label samples, and fluorophores are available that emit light in virtually any color. In a fluorescent microscope, a sample is labeled with a fluorophore, and then a bright light ( excitation light) is used to illuminate the sample, which gives off fluorescence ( emission light ).
Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy | Nikon's MicroscopyU It is important to note that fluorescence is the only mode in optical microscopy where the specimen, subsequent to excitation, produces its own light. The emitted light re-radiates spherically in all directions, regardless of the excitation light source direction.
Fluorescence Microscopy - Explanation and Labelled Images Fluorescence microscopy uses a high-intensity light source that excites a fluorescent molecule called a fluorophore in the sample observed. The samples are labeled with fluorophore where they absorb the high-intensity light from the source and emit a lower energy light of longer wavelength.
pubs.acs.org › doi › 10Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Super-Resolution Imaging Super-resolution imaging techniques that overcome the diffraction limit of light have gained wide popularity for visualizing cellular structures with nanometric resolution. Following the pace of hardware developments, the availability of new fluorescent probes with superior properties is becoming ever more important. In this context, fluorescent nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted increasing ...
Fluorescent Dyes | Science Lab | Leica Microsystems A basic principle in fluorescence microscopy is the highly specific visualization of cellular components with the help of a fluorescent agent. This can be a fluorescent protein - for example GFP - genetically linked to the protein of interest. If cloning is impossible - for instance in histologic samples - techniques such as immunofluorescence staining are used to visualize the protein ...
Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview - ScienceDirect Applications of single-molecule fluorescence microscopy. (A) The photophysical properties of a fluorophore contain information about its position and its state. This allows, for example, tracking molecules, observing conformational and constitutional changes, or following chemical reactions. (B) Examples for applications in biology and chemistry.
Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.
Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy Understanding cells as integrated systems is central to modern biology. Although fluorescence microscopy can resolve subcellular structure in living cells, it is expensive, is slow, and can damage cells.
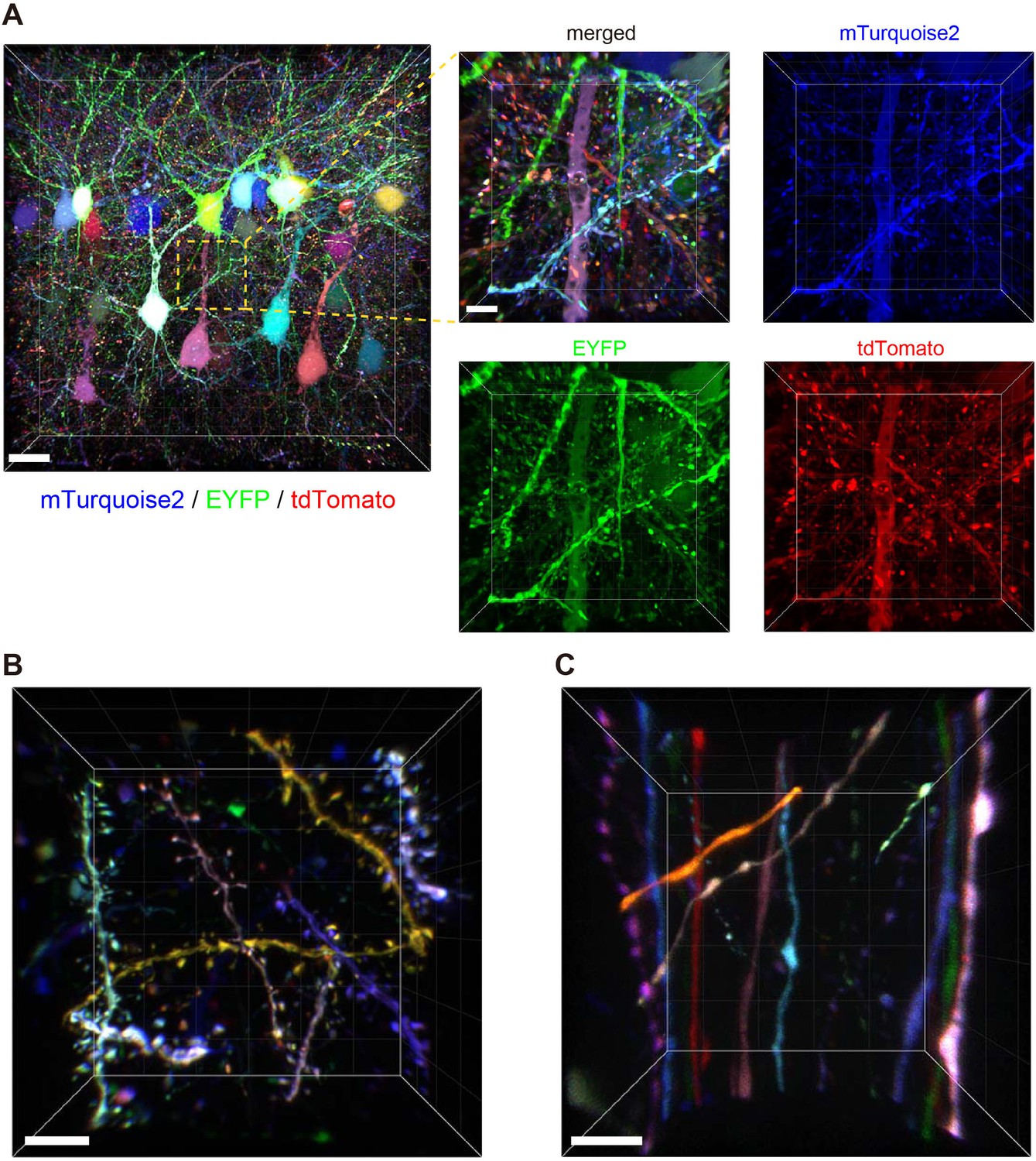
Different Ways to Add Fluorescent Labels - Thermo Fisher Scientific Using fluorescence provides greater contrast compared to viewing your samples with brightfield microscopy alone. Labeling various targets with separate fluorescent colors allows you to visualize different structures or proteins within a cell in the same experiment.
New fluorescent label provides a clearer picture of how DNA ... Unlike traditional fluorescence microscopy, which uses labels that glow constantly, this approach involves switching on only a subset of the labels at each moment. ... Discovery of 380-million ...
Fluorescent Labeling - What You Should Know - PromoCell Fluorescence microscopy allows the identification of cells and cellular components and the monitoring of cell physiology with high specificity. Fluorescence microscopy separates emitted light from excitation light using optical filters. The use of two indicators also allows the simultaneous observation of different biomolecules at the same time.
Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy • iBiology In this introductory lecture on light microscopy, Dr. Nico Stuurman describes the principles and properties of fluorescence microscopy. Skip to primary navigation; ... 00:01:04;23 so we label microtubules with the fluorescent dye 00:01:08;13 and we have part of the cell labeled in red, 00:01:11;25 and that part is actually the uh, nucleus
















Post a Comment for "44 fluorescent labels and light microscopy"